Data storage
Different storages can be used when running services on the DSRI:
🦋 Ephemeral storage: storage is bound to the pod, data will be lost when the pod is restarted or deleted (but this deployment does not require to request the creation of a persistent storage, and is faster to test code).
⚡ Dynamic storage: automatically create a persistent storage when starting an application. Can also be created in the OpenShift web UI, using the dynamic-maprfs Storage Class.
🗄️ Persistent storage: You can use a persistent storage volume to store data. Please see the Create the Persistent Storage section. You can do this yourself. Please keep in mind that there are no backups made of data on DSRI.
A storage (aka. Persistent Volume Claim) is only accessible in the project where it has been created.
Create the Persistent Storage
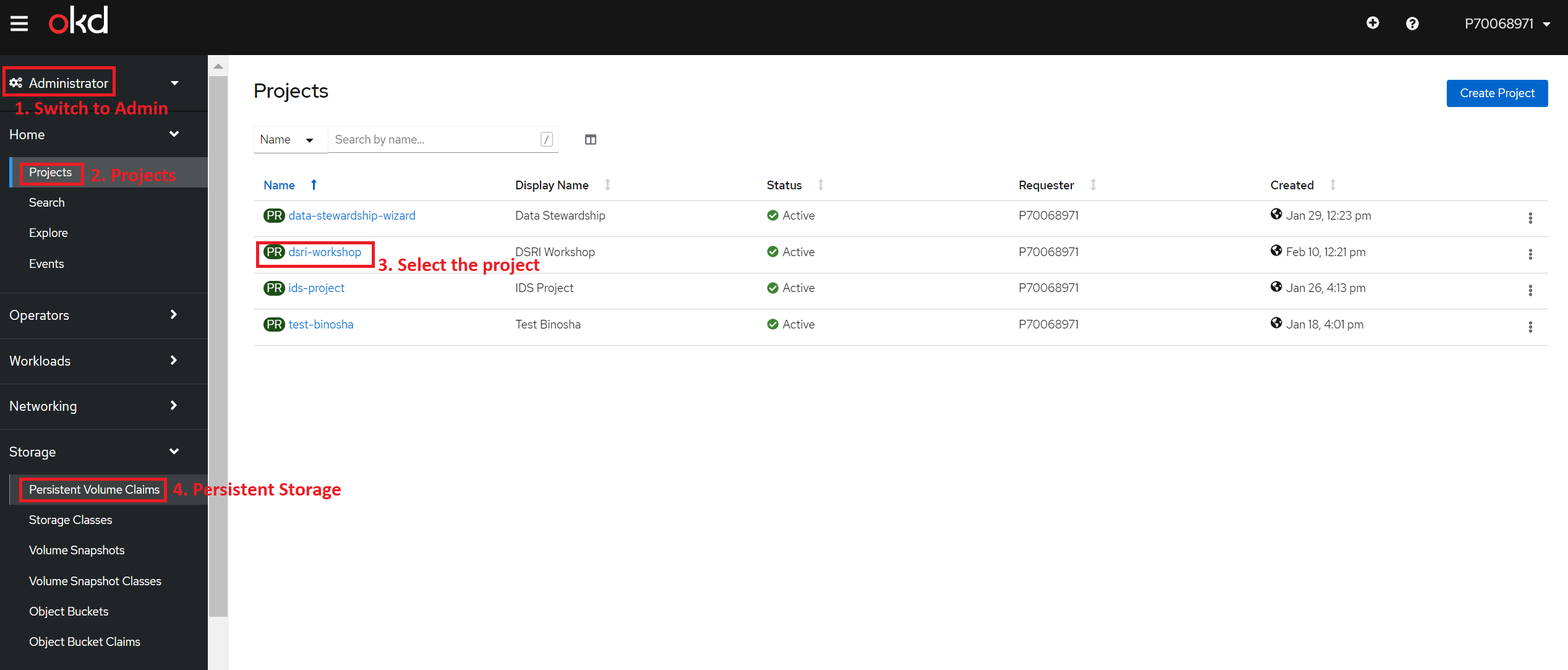
Switch to the Administrator view
Go to the Project panel
Select your project
Expand the Storage panel then go to the Persistent Volume Claim panel
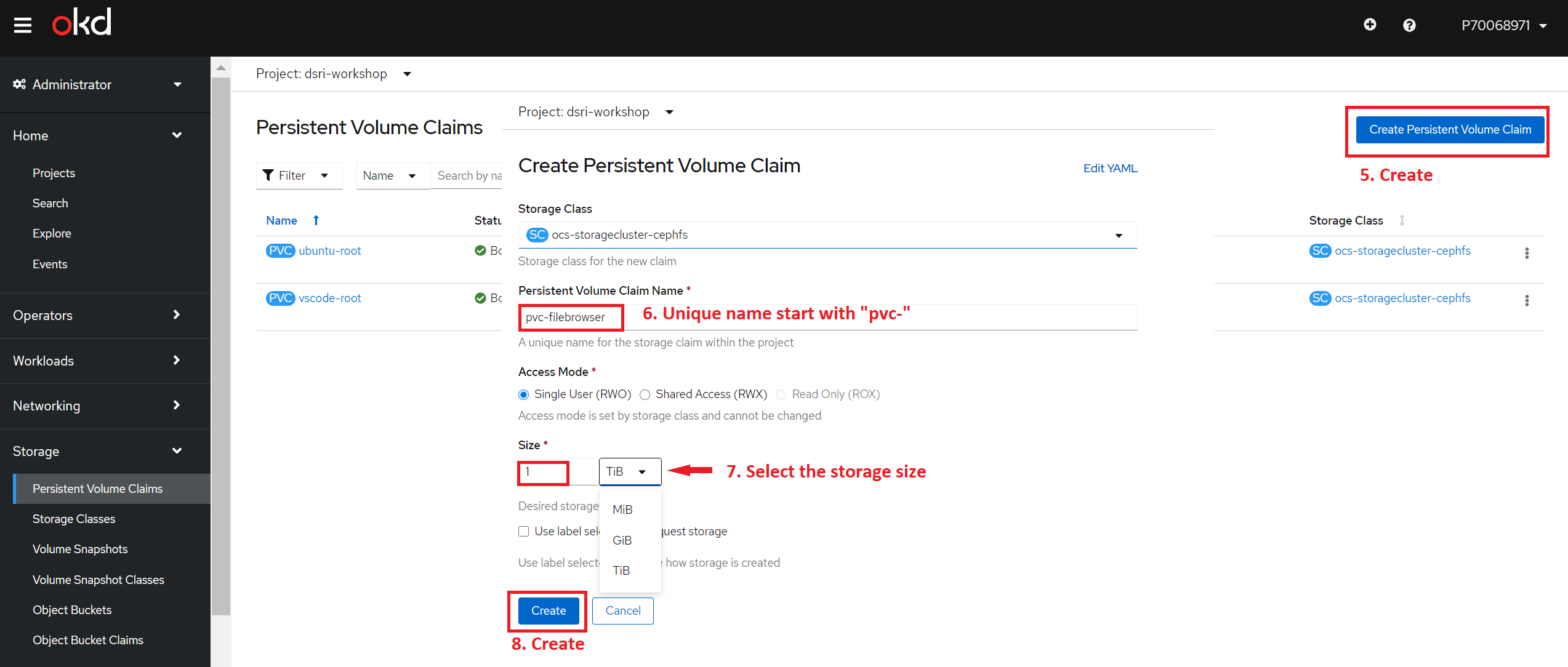
Click the button call Create Persistent Volume Claim
then you will redirect the wizard of Create Persistent Volume Claim
Choose the right storageClass! The default is
ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd, which is block storage and can be useful in some usecases. However, to be sure change this toocs-storagecluster-cephfs! Especially if you'd like to bind multiple pods to the PVC you are creating.Provide the unique Persistent Volume Claim Name start with
pvc-example:
pvc-filebrowserSelect the Access Mode
RWXand Storage SizeAccess Mode CLI abbreviation Description ReadWriteOnce RWOThe volume can be mounted as read-write by a single node. ReadOnlyMany ROXThe volume can be mounted as read-only by many nodes. ReadWriteMany RWXThe volume can be mounted as read-write by many nodes. Click Create
The DSRI using the Openshift Container Storage (OCS) which is based on CEPH offers ReadWriteOnce access mode.
ReadWriteOnce(RWO) volumes cannot be mounted on multiple nodes. Use theReadWriteMany(RWX) access mode when possible. If a node fails, the system does not allow the attached RWO volume to be mounted on a new node because it is already assigned to the failed node. If you encounter a multi-attach error message as a result, force delete the pod on a shut down or crashed node.
Static persistent volumes provides a sustainable persistent storage over time for applications that need to run regular Docker images (which usually use the root user).
Some Applications such as Jupyter template automatically creates a persistent storage
Connect the Existing Persistent Storage
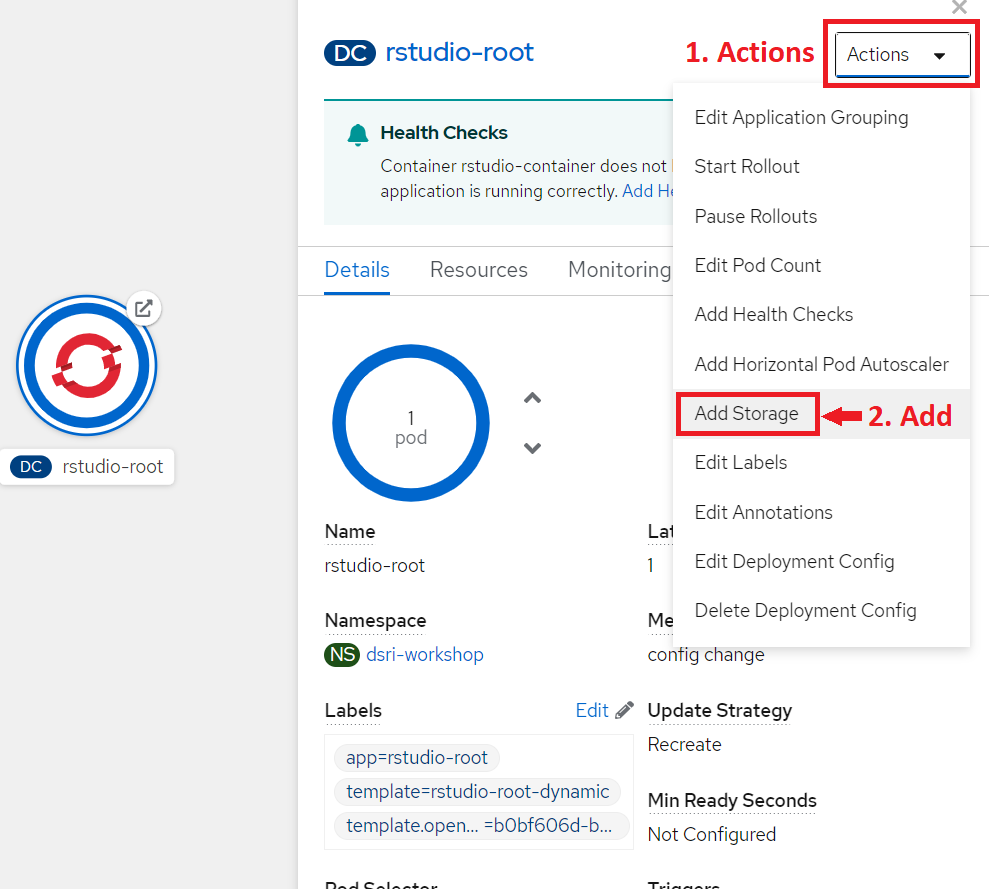
On the Topology page select your application,
Click Action on your application
Select the Add Storage option from the dropdown list.
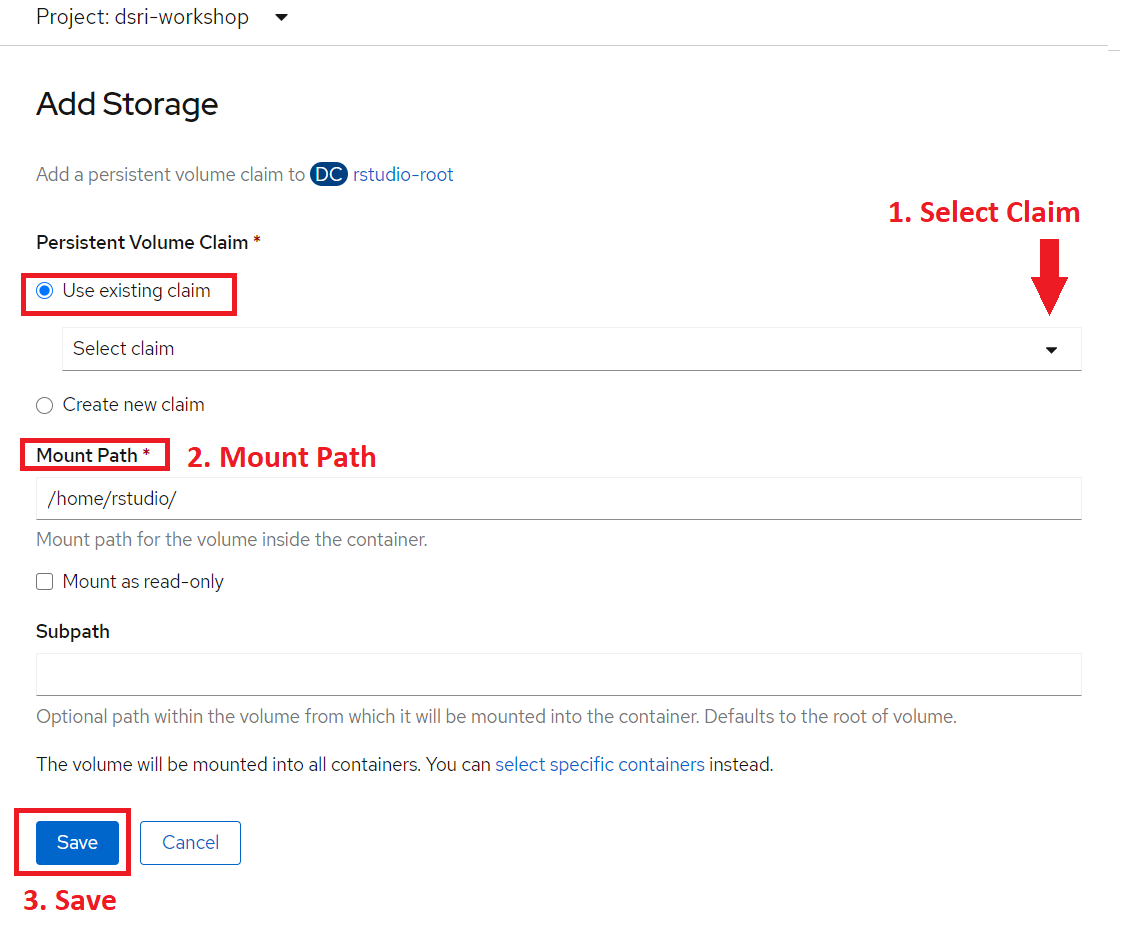
Select the Use Existing Claim option from the Add Storage wizard and Select the Claim
Add the Mount Path
Save
You can try above method if you want to connect more applications to the same storage
Expand existing Persistent Storage
Switch to the Administrator view
Go to the Project panel
Select your project
Expand the Storage panel then go to the Persistent Volume Claim panel
Click on the three dots (⋮) next to the Persistent Volume Claim you want to expand.
Click on Expand PVC in the menu.
Enter the size you want to expand your PVC with.
Hit Expand. It can take upto 2 minutes before your PVC is expanded.
Use the dynamic storage
Dynamic persistent volumes can be created automatically by an application template.
Dynamic storage can also be created manually, go to Storage on the left sidebar in a project:
- Click Create Storage top right of the Storage page.
- Storage class: ocs-storagecluster-cephfs
- Access Mode:
- Single User (RWO): only the user who created this volume can read/write to this volume.
- Shared Access (RWX): all users with access to the projects can read/write this volume.
- Read Only (ROX): all users with access to the projects can read this volume.
Use the ephemeral storage
We currently disabled this solution by default, as it was confusing for users and would lead to data loss.
When creating a pod, OpenShift will by default use ephemeral storage. It creates a volumes bind to the pod. So the volume will be deleted.
It is recommended to use dynamic provisioning for a more sustainable storage solution. But ephemeral storage can be sufficient for testing.