Glossary
Deployment
Usage: deployment(s) when speaking generally about Deployment or DeploymentConfig objects
A Deployment is a Kubernetes-native object that provides declarative updates for pods and replica sets.
A DeploymentConfig is an OpenShift-specific object that defines the template for a pod and manages deploying new images or configuration changes. Uses replication controllers. Predates Kubernetes Deployment objects.
When referencing the actual object, write as Deployment or DeploymentConfig as appropriate.
Docker
Docker can build images automatically by reading the instructions from a Dockerfile. A Dockerfile is a text document that contains all the commands you would normally execute manually to build a docker image.
Image stream
Image streams provide a means of creating and updating container images in an ongoing way.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes is a portable, extensible, open-source platform for managing containerized workloads and services, that facilitates both declarative configuration and automation. It has a large, rapidly growing ecosystem.
Kubernetes services, support, and tools are widely available.
Kubernetes, also known as K8s, is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
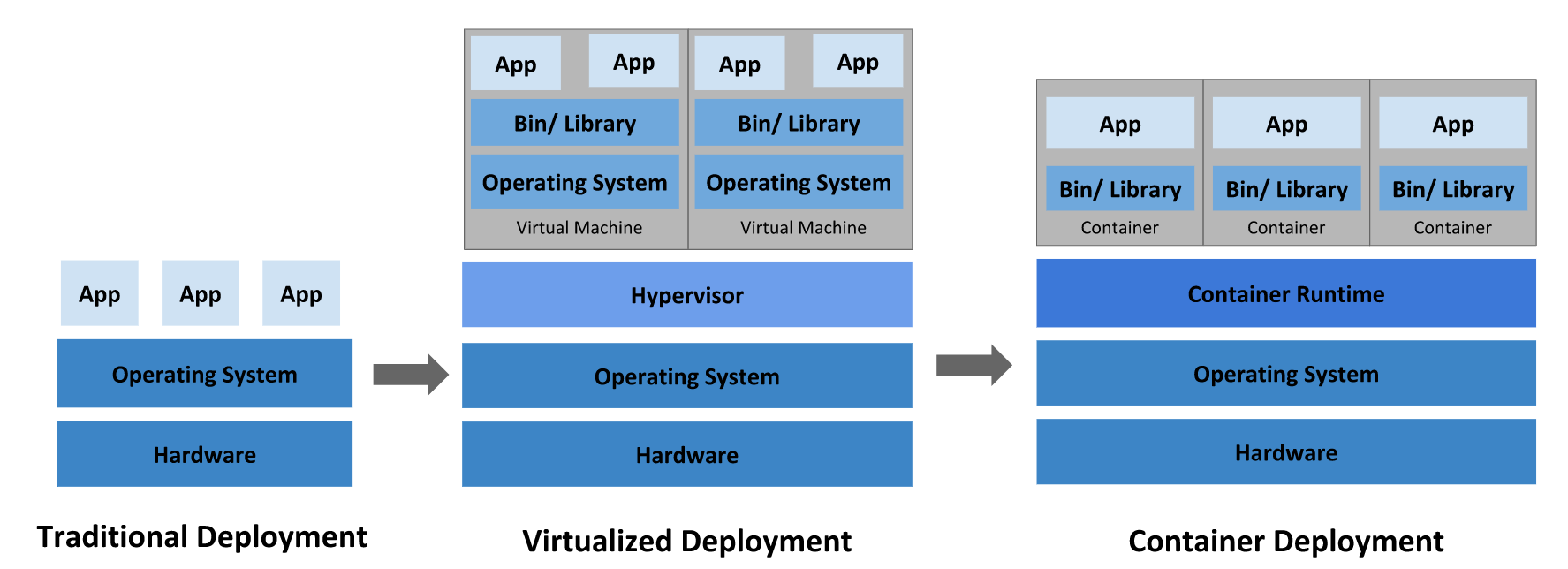
Node
A node is a worker machine in the OpenShift Container Platform cluster. A node is either a virtual machine (VM) or a physical machine.
OKD
OKD is a distribution of Kubernetes optimized for continuous application development and multi-tenant deployment. OKD adds developer and operations-centric tools on top of Kubernetes to enable rapid application development, easy deployment and scaling, and long-term lifecycle maintenance for small and large teams. OKD is a sibling Kubernetes distribution to Red Hat OpenShift
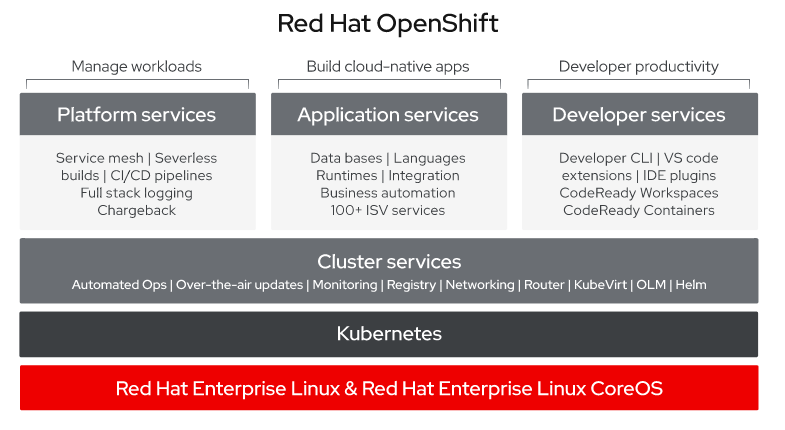
OpenShift
Red Hat OpenShift is a hybrid cloud, enterprise Kubernetes application platform, trusted by 2,000+ organizations.
It includes
- Container host and runtime
- Enterprise Kubernetes
- Validated integrations
- Integrated container registry
- Developer workflows
- Easy access to services
OpenShift CLI
The oc tool is the command-line interface of OpenShift 3 and 4.
When referencing as a prerequisite for a procedure module, use the following construction: Install the OpenShift CLI (oc).
Operators
Operators are the preferred method of packaging, deploying, and managing a Kubernetes application in an OpenShift Container Platform cluster. An Operator takes human operational knowledge and encodes it into software that is packaged and shared with customers.
Pod
A pod is the smallest logical unit in Kubernetes. A pod consists of one or more containers and runs on a worker node.
Project
A project allows a community of users to organize and manage their content in isolation from other communities. It is an extension of the Namespace object from Kubernetes.
Persistent volume claim (PVC)
Developers can use a persistent volume claim (PVC) to request a persistent volume (PV) resource without having specific knowledge of the underlying storage infrastructure.
Route
OpenShift-specific API object that allows developers to expose services through an HTTP(S) aware load balancing and proxy layer via a public DNS entry.
Secret
Kubernetes API object that holds secret data of a certain type.
Service
Kubernetes native API object that serves as an internal load balancer. A service is a named abstraction of software service (for example, mysql) consisting of local port (for example 3306) that the proxy listens on, and the selector that determines which pods will answer requests sent through the proxy.
Service Account
A service account binds together:
a name, understood by users, and perhaps by peripheral systems, for an identity
a principal that can be authenticated and authorized
a set of secrets