Deploy From a Docker Image
The DSRI is an OpenShift OKD cluster, based on Kubernetes. It uses Docker containers to deploy services and applications in pods.
Any service or job can be run in a Docker container. If you want to run a service in Python for example, you will find Docker images for Python.
- You can find already existing images for the service you want to run on DockerHub
- or create a custom Docker image in a few minutes.
Find an image for your service
The easiest way to deploy a service on the DSRI is to use a Docker image from DockerHub 🐳.
Search for an image for your service published on DockerHub
- Google "dockerhub my_service_name"
- Sometimes multiple images can be found for your service. Take the official image when possible, or the one most relevant to your use-case.
If no suitable image can be found on DockerHub, it can be deployed from a Dockerfile. See above to do so.
Deploy the image on DSRI
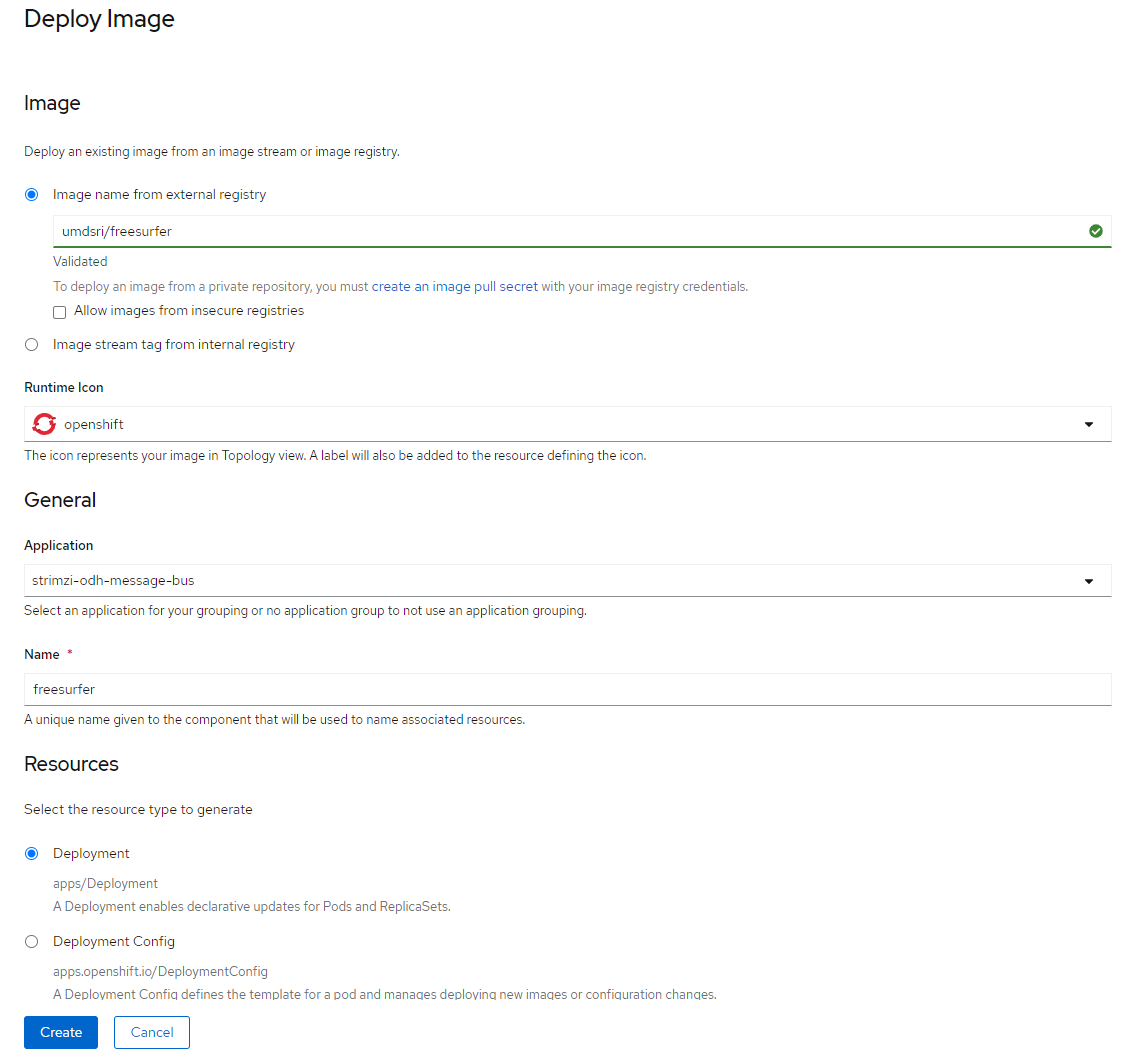
Once you have a Docker image for your application you can deploy it using the DSRI web UI.
Go to the Overview page of your project.
- Click the Add to Project button in top right corner > Deploy Image
- Select to deploy from Image Name
- Provide your image name, e.g.
umdsri/freesurfer - Eventually change the Name, it needs to be unique by project.
- Click Deploy.
- Provide your image name, e.g.
Once the application is deployed it will most probably fail because it has not been optimized to work with OpenShift random user ID. You will need to add an entry to the deployment to enable your image to run using any user ID.
Go to Topology, click on your application node, click on the Actions button of your application details, and Edit deployment. In the deployment YAML search for spec: which has a containers: as child, and add the following under spec:
spec:
serviceAccountName: anyuid
containers: ...
Build and push a new Docker image
In case you there is no Docker image for your application you can build and push one.
To build and push a Docker image you will need to have Docker installed.
Define a Dockerfile
If no images are available on DockerHub, it is still possible that the developers created the Dockerfile to build the image without pushing it to DockerHub. Go to the GitHub/GitLab source code repository and search for a Dockerfile, it can usually be found in
- the source code repository root folder
- a
dockersubfolder - as instructions in the
README.md
If no Dockerfile are available we will need to define one.
Feel free to contact us to get help with this, especially if you are unfamiliar with Docker.
Build the image
Once a Dockerfile has been defined for the service you can build it by running the following command from the source code root folder, where the Dockerfile is:
docker build -t username/my-service .
Arguments can be provided when starting the build, they need to be defined in the Dockerfile to be used.
docker build -t username/my-service --build-args MY_ARG=my_value .
Push to DockerHub
Before pushing it to DockerHub you will need to create a repository. To do so, click on Create Repository.
- DockerHub is free for public repositories
- Images can be published under your DockerHub user or an organization you belong to
Login to DockerHub, if not already done:
docker login
Push the image previously built to DockerHub:
docker push username/my-service
You can link DockerHub to your source code repository and ask it to build the Docker image automatically (from the Dockerfile in the root folder). It should take between 10 and 30min for DockerHub to build your image
You can also deploy a service on the DSRI directly from a local Dockerfile, to avoid using DockerHub. See this page to deploy a service from a local Dockerfile for more instructions